Database Connection
Database connections allows you to query your Summer warehouse from anywhere Arrow Flight SQL, and most places JDBC, are supported. This includes Python/Go programs, Jupyter notebooks, and BI tools like Grafana, DBeaver, or Tableau. Currently, database connections are read-only, writes coming soon.
Use this host:port when creating a database connection to Summer.
Creating your access token
Access tokens are required to connect to Summer via a database connection. To create a token, go to Summer -> User Settings -> Tokens.
We recommend creating a unique token for each tool or service you are connecting to Summer. When you create a token, make sure to copy it as you won’t be able to access it again. If you misplace a token, you can rotate or delete/recreate it. Tokens that are rotated out will continue to live for 1 hour.
Your token has the same permissions as your Summer user. Any dataset available to you via the web app will also be available to you over a database connection.
Example - Python
Here’s an example of querying Summer via Arrow Flight SQL in a Python script. This example utilizes uv for package management, but you can manage the script’s dependencies however you prefer.
Before we get started, you’re going to want to create a new Summer token and add it to your terminal environment variables. When you run the script in your terminal you’ll start the command with SUMMER_AUTH_KEY=$YOUR_SUMMER_KEY_ENV_VAR and just replace YOUR_SUMMER_KEY_ENV_VAR with the name you chose for your env variable.
# /// script
# requires-python = ">=3.13"
# dependencies = [
# "flightsql-dbapi",
# "polars",
# ]
# ///
import polars as pl
from flightsql import FlightSQLClient
import os
# Read in the Summer token from the env variables
key = os.environ['SUMMER_AUTH_KEY']
# Initiate an Arrow Flight SQL connection with Summer
client = FlightSQLClient(host="flight.summer.io",
port=443,
user="",
password=key,
)
# Enter the query you want to execute
query = """
SELECT
brand,
count(distinct key) as num_flavors,
avg(stars::INT) as avg_review,
count(*) as num_reviews
FROM
sample_data.icecream_reviews.reviews
GROUP BY
brand
ORDER BY
avg_review DESC
"""
# Using the connection with Summer, execute the query
info = client.execute(query)
# Retrieve the query results from the flight server
# Storing them in a FlightStreamReader object
reader = client.do_get(info.endpoints[0].ticket)
# Convert the results to a polars dataframe
# For a nice readable output
df = pl.DataFrame(reader.read_all())
print(df)Let’s break this down.
The script’s python dependencies are:
flightsql- the database connection protocol used to communicate with Summerpolars- used to structure the query results into a nice readable output format
This script is creating an Arrow Flight SQL connection using Summer’s flight.summer.io endpoint. Then issuing a standard SQL query to Summer’s flight server, retrieving the results, and printing them to the screen as a polars dataframe.
A note on the user parameter in the FlightSQLClient client connection: this should be left as the empty string "". The user parameter is not used by the server but many tools require it to be present.
To test for yourself, save the script as sample.py and run it using:
> SUMMER_AUTH_KEY=$PROD_SUMMER_KEY uv run sample.py
shape: (4, 4)
┌─────────┬─────────────┬────────────┬─────────────┐
│ brand ┆ num_flavors ┆ avg_review ┆ num_reviews │
│ --- ┆ --- ┆ --- ┆ --- │
│ str ┆ i64 ┆ f64 ┆ i64 │
╞═════════╪═════════════╪════════════╪═════════════╡
│ talenti ┆ 45 ┆ 4.311624 ┆ 4069 │
│ bj ┆ 57 ┆ 4.305804 ┆ 7943 │
│ hd ┆ 70 ┆ 4.218475 ┆ 4655 │
│ breyers ┆ 69 ┆ 4.027961 ┆ 5007 │
└─────────┴─────────────┴────────────┴─────────────┘Example - DBeaver
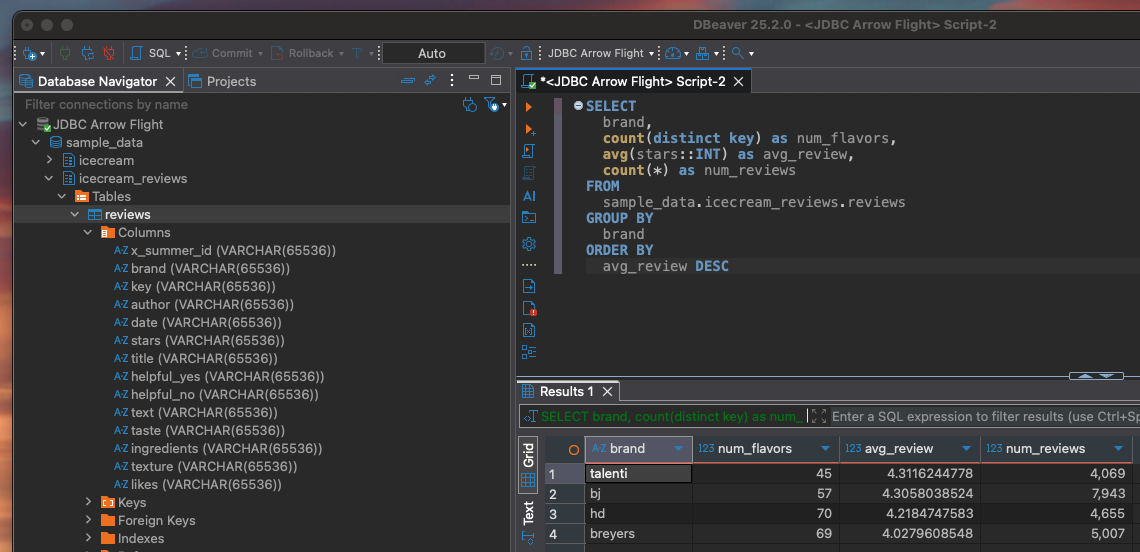
DBeaver is a well loved open source database management tool. This example will show how you can use DBeaver to connect to and query your Summer warehouse.
As with the previous example, the first thing you’ll need to do is create and retrieve an access token in Summer.
Next you’ll need to download and install the Arrow Flight SQL JDBC driver. Click here to download. Open DBeaver and under the Database menu select Driver Manager. Click New, enter Arrow Flight SQL JDBC in Driver Name. Then open the Libraries tab, click Add File, and select the downloaded flight-sql-jdbc-driver-17.0.0.jar file. Now click Find Class and select the first option org.apache.arrow.driver.jdbc.ArrowFlightJdbcDriver. Your driver is now configured!
Next we will create a Summer connection using the newly created driver. Click the New Database Connection button in the top left, double click the Arrow Flight SQL JDBC option and enter the following info:
- JDBC URL -
jdbc:arrow-flight-sql://flight.summer.io:443 - Username - Leave blank or use the word
username. This value is ignored on the server. - Password - Paste your token here
Click OK and double click the new Arrow Flight SQL JDBC item in your Database Navigator. This will attempt to connect to Summer, and when successfully connected, will populate the database navigator with your Summer warehouse schema organized by Org > Dataset > Table.
We will now enter the same SQL query from above,
SELECT
brand,
count(distinct key) as num_flavors,
avg(stars::INT) as avg_review,
count(*) as num_reviews
FROM
sample_data.icecream_reviews.reviews
GROUP BY
brand
ORDER BY
avg_review DESCClick execute SQL query and watch your query results enter the results table. You’re all set, you can now query any table you have access to in Summer via DBeaver.